Bone marrow is a soft, jelly-like tissue found in the center of your large bones — like your hip bone, ribs, and thigh bone (femur).
It’s basically your body’s blood cell factory, constantly working to produce billions of new cells every single day.
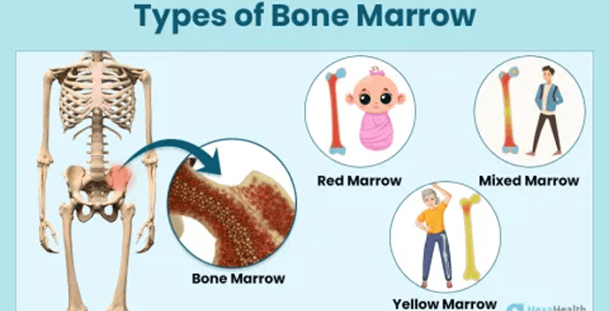
Types of Bone Marrow
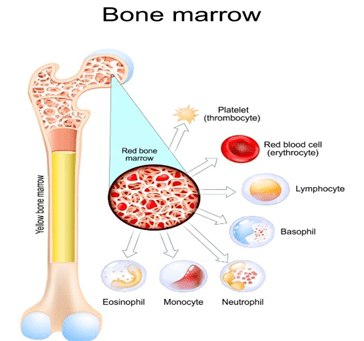
There are two types of bone marrow:
- Red marrow:
- Makes red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets.
- Found mainly in flat bones — like your skull, ribs, breastbone, and hip bones.
- Yellow marrow:
- Mostly made up of fat cells.
- Stores energy and can turn into red marrow when your body needs more blood (like during severe blood loss or infection).
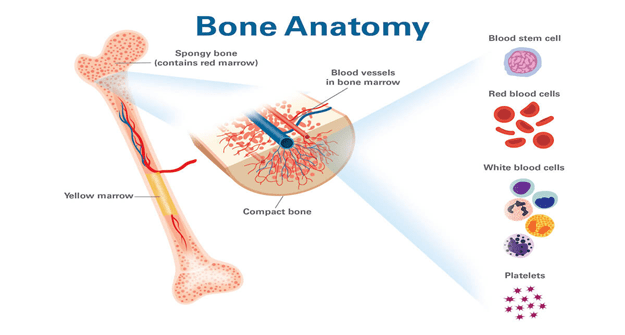
How Bone Marrow Works
Inside the marrow are stem cells — special “starter cells” that can grow into any kind of blood cell your body needs.
Here’s how they work:
- Stem cells divide and mature.
- They turn into RBCs, WBCs, or platelets.
- Once ready, they move into your bloodstream to do their job.
This process keeps happening your entire life — it’s how your blood stays fresh and balanced.
What Can Affect Bone Marrow
Bone marrow can be affected by:
- Cancers (like leukemia, myeloma)
- Infections
- Autoimmune diseases
- Toxic chemicals or radiation
- Certain medicines
- Nutritional deficiencies (like lack of Vitamin B12 or folate)
When it doesn’t work properly, your body may have:
- Too few blood cells (causing anemia, infection risk, or bleeding)
- Abnormal cells (as in cancers)
- Overproduction of one type of blood cell
Bone Marrow Transplant
Sometimes, when the marrow is too damaged to recover, doctors replace it through a bone marrow transplant (also called a stem cell transplant).
Healthy stem cells — from a donor or the patient’s own body — are used to rebuild normal bone marrow.
It’s a life-saving treatment for many serious blood and immune diseases.
How to Support Bone Marrow Health Naturally
You can’t control everything, but you can support marrow health with:
- Iron-rich foods: Spinach, lentils, red meat
- Vitamin B12 & folate: Eggs, milk, leafy greens
- Antioxidants: Berries, nuts, green tea
- Adequate sleep and exercise to boost blood circulation
- Avoid smoking and excess alcohol
Leave a comment